- Blogs
- Understanding Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Resistance & Fire Resistance Across Wool Insulations
Understanding Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Resistance & Fire Resistance Across Wool Insulations

In the construction industry, insulation is more than just a material choice—it is a performance indicator for energy efficiency, acoustic comfort, and fire safety. Among the different options available, glass wool and stone wool stand out as reliable mineral wool insulations.
To make informed decisions, stakeholders such as consultants, architects, OEMs, contractors, and end-users must clearly understand three fundamental performance parameters: Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Resistance and Fire Resistance.
Thermal Conductivity: The Basis of Thermal Performance
Thermal conductivity (λ-value) measure in Wm.K, indicates how easily heat passes through a material. The lower the thermal conductivity of the material, the better the insulation properties of it.
It is a property that varies with environmental temperature: as temperature rises, thermal conductivity increases.
- Glass wool offers very low thermal conductivity, performing slightly better than stone wool at lighter densities. It is ideal for ambient temperature applications.
- Stone wool , while slightly higher in λ-value, is preferred where high temperature performance is required.
Takeaway: For maximum thermal efficiency in standard applications, glass wool often provides the edge.
R-Value: Thickness Translated into Performance
Thermal resistance (R-value) measured in 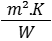 , is a measure of the thermal resistance of the built-up material against heat. It is directly proportional to the thickness of the insulation and inversely proportional to thermal conductivity. Higher R-value indicates better insulating performance.
, is a measure of the thermal resistance of the built-up material against heat. It is directly proportional to the thickness of the insulation and inversely proportional to thermal conductivity. Higher R-value indicates better insulating performance.
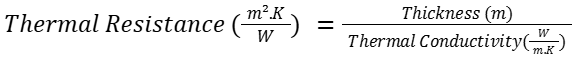
Takeaway: R-Value helps consultants and contractors balance design thickness, space availability, and performance targets.
Glass Wool: With its lower λ-value, glass wool achieves higher R-Values for the same thickness. For example, a 50 mm board can deliver an R-Value of ~1.66 m²·K/W.
Stone Wool: Due to slightly higher λ-value, the R-Value for the same thickness will be marginally lower, though it remains effective for applications where combined thermal and fire resistance are important.
Fire Resistance: Safety Beyond Energy Efficiency

Fire resistance refers to how insulation behaves under fire exposure, whether it contributes to flame spread, smoke emission, or structural failure.
Both glass wool and stone wool are considered as non-combustible insulation, typically rated Euro Class A1. It does act as a fuel to fie or release toxic smoke. There are multiple factors in which both the mineral wool insulations comply. Below mentioned are the standards one as a stakeholder should check for when buying the insulation for your space:
| S No | Standard | Type | Metric Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BS 476 Part 4 | Non-Combustibility Test | Determines whether a material is non-combustible when exposed to fire, ensuring it will not contribute to flame spread |
| 2 | BS 476 Part 5 | Non-Ignitability Test | Assesses how easily a building material can ignite when exposed to a small flame source |
| 3 | BS 476 Part 6 | Fire Propagation Test | Measures how much a material contributes to the growth and spread of fire through heat release |
| 4 | BS 476 Part 7 | Surface Spread of Flame Test | Classifies materials based on the rate and extent to which flames spread across their surface |
| 5 | BS 6853 | Smoke Fume Test | Specifies fire safety requirements for materials used in railway interiors, focusing on passenger safety during a fire |
| 6 | ASTM E84 | Surface Burning – Steiner Tunnel Test | Evaluates flame spread index and smoke developed index, widely used to classify building materials for fire performance |
However, for high temperature applications, stone wool is often preferred due to its high temperature fire resistance. Glass wool can be used up to 230oC while stone wool can be used up to 750oC making it a preferred product in drywall and façade applications in buildings.
Takeaway: Both insulations ensure compliance with stringent fire codes, but stone wool is often chosen for projects requiring extended fire endurance.
Key Considerations for Decision Makers
When selecting insulation materials, the balance lies in matching project needs with performance priorities:
- Choose glass wool for energy efficiency, acoustic comfort, and ease of installation.
- Choose stone wool when fire endurance and high-temperature stability are the top criteria.
In both cases, compliance with EN, BS and BIS standards ensures reliability, safety, and long-term performance.
Conclusion:
Understanding thermal conductivity, thermal resistance and fire resistance isn’t just about numbers—it’s about shaping buildings that are efficient, safe, and built to last.
Both glass wool and stone wool bring strong performance to the table, but the best choice depends on the unique demands of each project. For consultants, architects, and contractors, the right insulation decision starts with understanding performance, not just products, because when design meets the right material, the result is safer, more comfortable, and future-ready spaces.
If you are looking to learn more or have a query about insulation solutions, feel free to reach out to us at sgindia.insulation@saint-gobain.com”.
Latest Blogs




